Pelletizing, a form of tumble growth agglomeration, continues to be employed in an increasing number of applications, lending an array of benefits to raw materials, end products, and production lines.
As demand for nickel continues to rise in the transition to a low-carbon economy, pelletizing is gaining more interest for its application in recovering dust produced during the processing of nickel laterite ores to produce ferronickel.
Here’s a look at how pelletizing is helping producers to make the most out of their nickel ore sources.
Nickel Dust Generation From Laterites
Nickel-laden dust and fines are generated throughout the nickel laterite mining and processing lifecycle:
Initial Handling & Crushing
Nickel laterites are generally recognized as containing a high amount of fines. Further, as part of the initial ore dressing process, laterites are crushed and screened, which generates additional fines.
Dust in Off-Gases
Most laterite ores are processed via the Rotary Kiln Electric Furnace, or RKEF method, which takes a pyrometallurgical approach to nickel beneficiation. This method of processing can be summarized as follows:
- Crushed nickel ore is first dried to remove free moisture, a process typically carried out in a rotary dryer.
- The dried ore is then reduced and calcined in a rotary kiln to remove chemically bound moisture, partially reduce nickel and iron, and preheat the ore.
- The calcined ore is further reduced and smelted in an electric furnace.
A disadvantage to this approach is that at each step, and particularly during calcination, a significant amount of nickel-bearing dust is produced and collected through off-gas equipment.
General Handling
In addition to the dust generated during crushing and collected from off-gases, dust may also be generated during handling and transitions between each step due to the friable nature of laterites, further adding to the problem.
The amount of nickel contained in this dust can be substantial, making recovery of the remaining nickel attractive, particularly given its rising demand. As such, there is a high incentive to recover the nickel from this dust, and pelletizing has emerged as the preferred approach to facilitating recovery.
About Pelletizing Nickel Dust
Pelletizing is a form of tumble growth (agitation) agglomeration or wet granulation that utilizes motion paired with a liquid binder to transform fines into rounded pellets.
The pelletizing process works as follows: fines are combined with a liquid binder in order to create a homogeneous mixture for pellet formation. The mixture, along with additional binder, is continuously fed to the pelletizing device where the agitation and binding agent join forces to cause a layering effect known as coalescence. At this stage, the pellets are in a wet state and referred to as “green pellets,” which are then heat hardened prior to smelting.
The pellets are retained in the unit until they reach the desired size, at which point they are discharged.
As with iron ore pelletizing (often referred to as balling), nickel dusts are typically pelletized using either a rotary drum or disc pelletizer, with the latter being more common.
Disc Pelletizers
Disc pelletizers, also known as pan pelletizers or pan granulators, are one of the most commonly employed types of equipment for carrying out the pelletizing process.
The disc pelletizer consists of a rotating pan mounted onto a stationary base. The pan is equipped with a spray system for the addition of binder. Centrifugal force carries pellets through the spray and feed areas to promote layering.
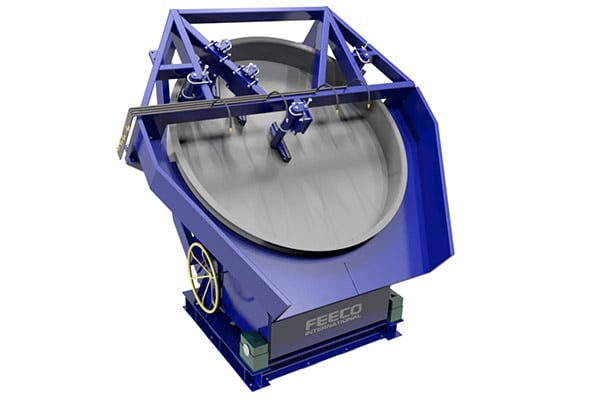
3D Rendering of a FEECO Disc Pelletizer for pelletizing nickel ore
Disc pelletizers are often chosen for their high level of size control and their ability to produce refined round pellets.
Rotary Drums
Rotary drums, sometimes called balling drums in this context, also serve as an effective pelletizing tool.
The rotary drum consists of a large, rotating drum set on a slight angle to assist material in moving through the drum via gravity. Again, material and binder are continuously fed to the unit, where rotation and the binder promote layering of seed pellets.
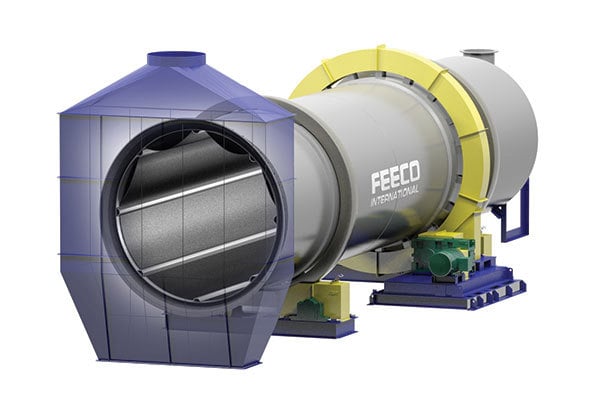

3D Rendering of a FEECO Rotary Drum for pelletizing nickel ore
Rotary drums are chosen for their high-capacity throughput and because they are a closed system.
More information on choosing between a disc pelletizer and rotary drum >>
Benefits to Pelletizing Recovered Nickel Dusts
A number of studies have been conducted over the years to demonstrate the advantages of pelletizing recovered nickel dusts, and the success of these trials and subsequent uses continues to lead to increased adoption.
First and foremost, the practice has obvious environmental, social, and economic advantages. Environmentally and socially, nickel dust generated at smelting sites can be recovered instead of stored in heaps, as has traditionally been common management practice. This prevents the nickel and other heavy metals from contaminating the surrounding environment and its inhabitants.
Economically, pelletizing allows producers to maximize nickel recovery from ore sources during a time when demand for nickel has never been higher.
A few other benefits have contributed to the growing use of nickel dust pelletizing as well:
Reduced Degradation in the Smelter Due to Improved Crush Strength
One major advantage of pelletizing is the opportunity to improve the smelting process.
The practice of pelletizing allows the crush strength of agglomerates to be controlled. This helps to ensure pellets will be able to withstand the charge weight in the furnace and won’t break down into fines that would degrade performance by inhibiting air flow through the material bed.
Other factors such as size and composition can also be influenced through pelletizing.
Flexibility
The flexible nature of the pelletizing process and the incorporation of multiple feeds is beneficial because it allows other sources of finely divided ores or beneficial additives to be incorporated.
Conclusion
As nickel’s role in the energy transition continues to grow, recovering dusts from laterite ores via pelletizing will become an increasingly important tool in maximizing nickel resources. This approach is already in use at commercial scale, including at the Barro Alto mine where FEECO disc pelletizers produce nickel pellets from reclaimed dust.
FEECO is the world’s premiere provider of custom disc pelletizers and complete pelletizing lines. The FEECO Innovation Center offers batch- and pilot-scale testing capabilities for assessing feasibility and gathering the process data necessary for scale-up. We also offer a comprehensive parts and service program, including pelletizer training. For more information, contact us today!


