Pin mixers offer an effective approach to mixing, de-dusting, and agglomerating solid and liquid feed components. What follows are some of the most frequently asked questions (FAQs) surrounding these diverse continuous mixers.
How does a pin mixer work?
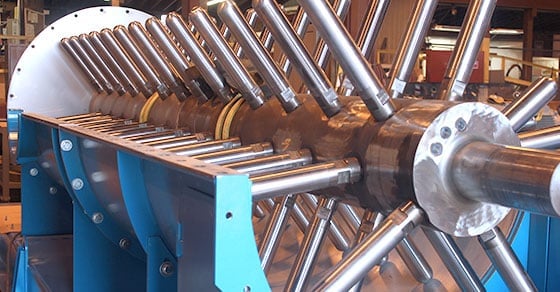
A pin mixer consists of a horizontal shaft enclosed in a stationary trough. The shaft spins at a specified speed, typically at several hundred rotations per minute (RPMs), for a predetermined retention time. Solids are fed into the inlet while a spray system distributes the liquid component over the material bed.
The shaft is fitted with pins or rods, which extend outwardly from the shaft. As the shaft spins, the solid and liquid components are thoroughly mixed. Learn more on pin mixer operating theory >>
Does a pin mixer produce granules?
A pin mixer can produce a range of material consistencies depending on the desired output. This ranges from a homogenized powder blend, to a wet “fluff,” as well as micro pellets/granules in the range of 20-60 mesh.
What objectives can pin mixers achieve?
Pin mixers are incredibly diverse and can achieve a wide range of objectives, including de-dusting/material conditioning, micro pelletizing, and homogeneous mixing of solid and liquid components. They are widely used for mixing applications, as well as conditioning material and forming seed pellets prior to another agglomeration device (most often a disc pelletizer or extruder).
What mode of action does the pin mixer use?
The pin mixer is a medium-shear mixer that utilizes a high-speed spinning action that imparts centrifugal force to homogeneously mix solid and liquid components.
Are pin mixers batch or continuous?
Pin mixers are continuous horizontal mixers, making them an ideal fit for large-scale applications requiring a high throughput.
What’s the difference between a pin mixer and a pugmill mixer?
While pin mixers and pugmill mixers are both horizontal mixers, they have a variety of differences that make each suited to different applications.
The primary difference lies in the mixing motion: pin mixers utilize a single spinning shaft, while pugmill mixers use a dual-shaft design to yield a folding or kneading motion. Because of this spinning action, pin mixers are also better suited for operations that require greater material densification; the high-speed spinning is better at densifying material than the folding motion of the pugmill mixer.
Pin mixers also have a lower torque than pugmill mixers, making them less appropriate in situations where tramp material is common, as this could become lodged between the pins and trough wall, causing damage.
For more information on the differences between these two industrial mixers, see our article, Choosing an Industrial Mixer: Pin Mixer or Pugmill Mixer.
What is the material retention time?
Retention time is largely a result of the desired output, or in other words, the time required to achieve a homogeneous mixture, or pellets of the desired size and density. This makes retention time highly application-specific. In general, however, retention time typically falls somewhere in the range of 15 seconds.
What are the normal wear items?
As the component most in contact with the material, the pins exhibit the most wear. The shaft and trough liner may also wear, but to a much lesser extent, unless working with a highly abrasive or corrosive material, though options for combatting such wear are available.
Can pin mixers be customized?
Pin mixers offer ample opportunity for customization. This includes the use of various pin arrangements, materials of construction, spray system designs, cover assemblies, drive assembly types, and more. The extensive ability to customize a pin mixer according to specific material and process requirements has lent this industrial mixer to a wide range of applications.
Can pin mixers be automated?
Yes, pin mixers are easily automated to assist operators in start-up and shutdown. More advanced automation and control systems are also available for operators looking for greater process transparency and more control over production parameters.
What applications are best for a pin mixer?
Pin mixers are ideal for homogeneously mixing solid and liquid components. Their high-speed spinning action works especially well with ultra-fine materials such as carbon black, pigments, ceramics and clays, gypsum, and limestone (for this reason, they are widely used as a preconditioning device in soil amendment plants).
How do I know if a pin mixer is right for my application?
In general, manufacturer expertise can help to determine if a pin mixer is the best fit for a given application. However, in some cases, feasibility testing in a facility such as the FEECO Innovation Center may be necessary to confirm that a pin mixer will meet the intended objectives. Once proof of concept is shown, testing can be used to gather process data points for building the commercial-scale unit and operating it on a continuous basis in a production setting.
What are the benefits of using a pin mixer as a preconditioning device prior to a disc pelletizer?
Pin mixers are frequently used prior to a disc pelletizer as a way of conditioning material prior to the primary agglomeration device. This approach can lend a number of benefits:
- Increased production
- Reduced binder costs (resulting from the pin mixer’s ability to increase density via motion)
- Improved flowability of feedstock onto the disc pelletizer
- More uniform product due to a more even distribution of the binder
Conclusion
Pin mixers offer industrial processors an effective approach to mixing, conditioning, de-dusting, and more. While many questions can arise in evaluating the use of a pin mixer, working with an expert, as well as vetting the process through testing, can help to ensure the best possible solution.
FEECO is the world’s leading pin mixer manufacturer for applications of all kinds. Backed by process development testing and comprehensive parts and service support, companies around the globe continue to choose FEECO pin mixers. For more information on our custom pin mixers, contact us today!