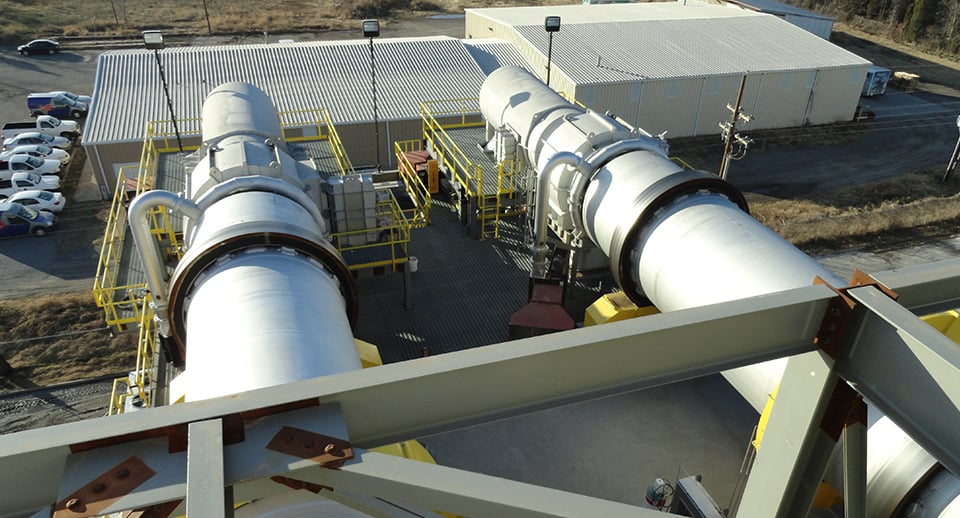
FEECO is a leading manufacturer of highly engineered, custom rotary kilns for processing solids. Our high-temperature kilns have earned a reputation for their durability, efficiency, and longevity.
Based on rotary drum technology, a rotary kiln consists of a large rotating cylinder (the drum) fitted with tires resting on trunnion wheels that help to facilitate rotation via a drive assembly. The horizontal drum is positioned on a slight slope to allow gravity to assist in moving material through the unit. Material is processed according to predetermined temperature profiles and retention times in order to cause a physical change or chemical reaction.
The high temperatures required in rotary kiln processing, combined with heavy loads, mean rotary kilns must be designed to withstand significant thermal stressors, requiring expertise in both engineering and fabrication.
Rotary kilns are available in direct- and indirect-fired configurations, the choice between which depends on the material properties, as well as the intended reaction.
DIRECT-FIRED ROTARY KILNS
Direct-fired kilns utilize direct contact between the material and process gas to efficiently process the material. Combustion can occur in a combustion chamber to avoid direct flame radiation, or the flame can be directed down the length of the kiln. Material is heated via contact with the gas stream.
Direct-fired kilns can be of the co-current (parallel) or counter-current configuration, referring to the direction the combustion gasses flow in relation to the material.
FEATURES
- Size: Up to 15′ diameter x 100’+ long (Up to 4.6m dia. x 30.5m+ long)
- Capacity: 1 TPH – 50 TPH (1 MTPH – 45 MTPH); maximum capacity is dependent on process variables unique to each application
- Parallel or counter-current flow
- Optimized Refractory Lining Solutions (multiple layers, castable, brick)
- Engineered shell to eliminate distortion and misalignment due to high operating temperatures
- Various Drive Assemblies Available
Optional Components
- Various Seal Options
- Machined Bases
- Screw Conveyor Feeder
- Automatic Gear Lubrication System
- Exhaust Gas Handling Equipment
- Ductwork
- Various Burner Configurations
- Components for increasing efficiency (flights, dams, bed disturbers, etc.)
Accommodates Various Fuel Types
- Fuel Oil
- Natural Gas/Propane
- Waste Heat
- Biogas
Material Options
- Carbon Steel

FEECO is capable of meeting the requirements necessary for CE marking equipment.

All FEECO equipment and process systems can be outfitted with the latest in automation controls from Rockwell Automation. The unique combination of proprietary Rockwell Automation controls and software, combined with our extensive experience in process design and enhancements with hundreds of materials provides an unparalleled experience for customers seeking innovative process solutions and equipment. Learn more >>
In addition to the rotary kiln itself, FEECO can supply a complete system with services, including:
- Material Handling
- Agglomeration
- Drying
- Afterburner / SCC
- Quench Tower
- Baghouse / Scrubber
- Acid Gas Removal
- Product Cooling
- Field Assistance / Installation
- Field Assistance / Start-up
DIRECT-FIRED ROTARY KILN COMPONENTS AND PARTS
The image below shows the standard components of a direct-fired rotary kiln. Click image to view larger.
Mechanical Construction of a Rotary Kiln (3D Rotary Kiln by FEECO International)
A – Discharge Breeching
B – Riding Ring/Tire
C – Refractory Lining
D – Gear/Sprocket Guard
E – Counter Current Exhaust System
F – Inlet Chute
G – Inlet Breeching
H – Leaf Seal
I – Drive Base
J – Drive Chain
K – Pinion/Drive Sprocket
L – Pillow Block Bearing
M – Gear Reducer
N – Girth Sprocket
O – Drive Motor
P – Trunnion Base
Q – Drum Shell Riding Ring
R – Graphite Block Lubrication Assembly
S – Trunnion Wheel
T – Trunnion Guard
U – Pillow Block Bearing
V – Thrust Roller Assembly
W – Discharge Chute
X – Burner
INDIRECT-FIRED ROTARY KILNS
Indirect-fired kilns are used for various processing applications, such as when processing must occur in an inert environment, when working with finely divided solids, or when the processing environment must be tightly controlled.
An indirect-fired kiln is enclosed in a furnace, which is then externally heated. The material is heated via contact with the kiln shell.
FEATURES
- Size: Up to 15′ diameter x 75’+ heated length (up to 4.6m dia. x 23m+ heated length) maximum capacity is dependent on process variables unique to each application
- Capacity: 1 TPH – 20 TPH (1 MTPH – 18 MTPH)
- Heat resistant alloy shell
- Engineered shell to eliminate distortion and misalignment due to high operating temperatures
- Separate zones for temperature control
- Integrated cooling zone can be added
- Various Drive Assemblies Available
Optional Components
- Various Seal Options
- Machined Bases
- Screw Conveyor Feeder
- Automatic Gear Lubrication System
- Ductwork
- Components for increasing efficiency
- (flights, dams, bed disturbers, etc.)
- Internal Bed Temperature Measurement
Accommodates Various Fuel Types
- Fuel Oil
- Natural Gas/Propane
- Electricity
- Waste Heat
- Biogas
Material Options
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Specialty Alloys
- Cladded Steel
- AR Steel
INDIRECT-FIRED ROTARY KILN COMPONENTS AND PARTS
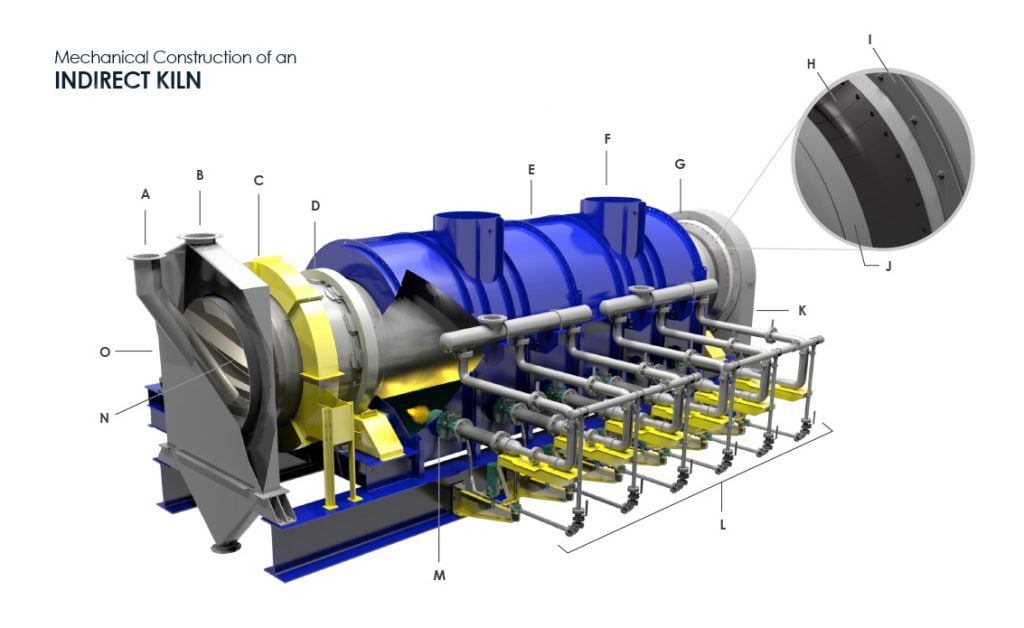
The image below shows the standard components of an indirect-fired rotary kiln. Click image to view larger.
Mechanical Construction of an Indirect Rotary Kiln (3D Indirect Rotary Kiln by FEECO International)
A – Material Inlet
B – Kiln Exhaust
D – Gear/Sprocket Guard
D – Riding Ring
E – Furnace
F – Furnace Exhaust Vent(s)
G – Air Seal
H – Spring/Leaf Seal
I – Seal Mounting Flange
J – Seal Wear Surface
K – Discharge Breeching
L – Gas and Air Piping
M – Burners
N – Advancing Flights
O – Inlet Breeching
APPLICATIONS & MATERIALS
Rotary kilns are versatile thermal processing machines capable of processing a wide variety of materials. Common applications for rotary kilns are listed below.
CALCINATION
Calcination refers to the process of heating a material to a temperature that will cause chemical dissociation (chemical separation). This process is used frequently in the creation of inorganic materials.
PYROLYSIS
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of a material in the absence of oxygen. For this reason, pyrolysis is typically carried out in an indirect rotary kiln, where the processing environment inside the kiln can be tightly controlled. Pyrolysis is widely used in the recycling industry to facilitate the conversion of plastics to fuel (PTF).
THERMAL DESORPTION
Thermal desorption is also a separation process. This process uses heat to drive off a volatile component, such as a pesticide, from an inorganic mineral, such as sand. It is also widely used in the regeneration of spent catalysts. The target component(s) are vaporized at the increased temperature, causing a separation without combustion. In some cases, an indirect rotary kiln would be best for this application, because the volatile chemicals may be combustible. The indirect kiln will supply the heat for desorption, without the material coming into direct contact with the flame.
ORGANIC COMBUSTION
Organic combustion refers to the treatment of organic wastes with the intent of reducing mass and volume. Organic waste is treated in the kiln, leaving behind an ash with considerably less mass and volume.
REDUCTION ROASTING
Reduction roasting is the removal of oxygen from a component of an ore usually by using carbon monoxide (CO). The CO is typically supplied by mixing a carbonaceous material such as coal or coke with the ore or by feeding it separately. Examples are the reduction roasting of a hematite-containing material to produce magnetite that can be magnetically separated.
Some of the most common materials for which rotary kilns are employed include:
- Activated Carbon
- Alumina
- Lithium Battery Chemicals & Recycling
- Catalysts
- Electronic Waste
- Phosphate Ore
- Plastic Waste
- Pigments
- Precious Metals
- Proppants
- Roofing Granules
- Specialty Ceramics
- Specialty Chemicals
- Waste Lime Sludge
- Waste Materials
ROTARY KILN PROCESS DEVELOPMENT
As the industry’s leading custom rotary kiln manufacturer, FEECO offers a unique pilot plant and testing facility where we use batch- and pilot-scale kilns to establish process and equipment criteria for reaching your production goals.
PARTS & SERVICE sUPPORT
Our Customer Service Team has an extensive offering of parts and services to keep your rotary kiln running its best for years to come.
RESOURCES
ROTARY Kiln ARTICLES

From Waste to Resource: The Role of the Pyrolysis Kiln in Black Mass Recycling
The pyrolysis kiln looks to be an effective approach in recycling black mass – the powdery mixture of key battery minerals …

Making the Switch from Reactive to Preventive Maintenance
The benefits of a preventive maintenance program are well documented – reduced downtime, lower maintenance costs, improved safety, and longer equipment …