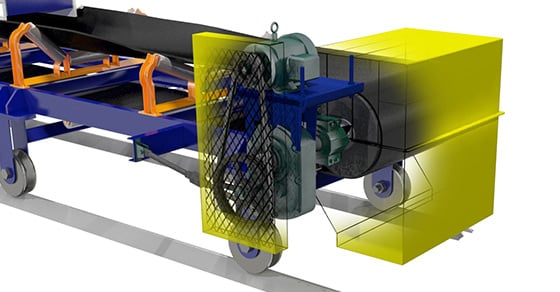
As the driving power behind a troughed belt conveyor, the drive assembly is a critical component in a conveyor’s ability to perform reliably and efficiently in the long term.
Also known as the drive arrangement, the drive assembly is what supplies the torque to create the necessary motion for the pulley to move the conveyor belt. The drive assembly consists of several components, but is primarily considered as the motor and reducer.
Selecting the proper drive assembly for the intended application is essential to minimizing downtime, streamlining maintenance procedures, and ensuring optimal belt conveyor performance. What follows is an overview on the types of drive assemblies available for belt conveyors, as well as some of the considerations to keep in mind when designing or purchasing a new belt conveyor or other bulk material handling equipment.
Why Drive Assembly Selection is Important
As a key contributor to conveyor performance and longevity, as well as overall efficiency, selecting the right drive assembly for a given task is crucial. Troughed belt conveyors and other bulk material handling equipment are tasked with a variety of jobs throughout various industries, from handling wood chips and biomass, to transporting ores, fertilizers, and more.
This diverse set of handling requirements necessitates an equally diverse solution to powering a belt conveyor; a drive assembly for a conveyor handling shredded paper has significantly different needs than one designed for ore handling at a mine site. As such, drive assemblies are available in a variety of configurations, each suited to different demands.
Selecting an under-powered drive assembly will eventually require replacement of the unit with something more adequate. Selection of an overpowered drive assembly may seem like a safer option, but incurs substantially higher operating costs over time. Additionally, since cost increases with horsepower requirements, larger drive assemblies require a greater capital investment, making an oversized drive assembly a costly alternative.
What’s Important in a Conveyor Drive Assembly?
Belt conveyors allow facilities to keep production moving. This necessitates two key criteria that conveyor drive assemblies must offer:
Reliability
Plant operators demand a high level of reliability from their conveyor assemblies. If the drive assembly isn’t reliable, it can cause a process upset or shutdown, holding the entire operation hostage and resulting in material backlogs and other problems.
As bulk material handling systems must work tirelessly, often without stopping, for months at a time, drive assemblies must remain dependable for long-term operation.
Reliability is often achieved by selecting a reputable equipment supplier that has the expertise to size and design the drive assembly according to the precise demands of the application, ensuring the unit is fit for the level of duty in the long-term.
Factors such as the hours of operation, material bulk density, whether or not the unit will be started under load, how frequently the unit will be cycled (started and stopped), as well as environmental factors such as plant elevation, ambient temperature, humidity, and more, will all influence drive assembly design.
Simplified, Minimal Maintenance
While conveyor drive assemblies generally require minimal maintenance, they do depend on regular upkeep such as routine oil changes and visual inspections, as well as temperature and vibration monitoring systems to ensure long-term reliability. For this reason, drive assemblies must be easily accessible to maintenance personnel, allowing them to conduct any necessary procedures or troubleshooting safely and without issue.
Safety
Drive assemblies are made up of moving parts such as rotating shafts and couplings that require proper guarding to minimize the potential for injury. High-speed V belts also require guarding.
Efficient
Drive assemblies should be designed to be as energy efficient as possible to minimize unnecessary energy costs. As mentioned, selecting an overpowered drive assembly may seem like a good option, but can incur much higher operating costs over time.
Conveyor Drive Assembly Options
FEECO utilizes several base model drive assemblies as a platform for creating custom drive assemblies suited to the specific project demands of the application at hand. As FEECO designs bulk material handling equipment for everything from specialty chemicals to mineral processing, we start with already-robust drive assembly configurations. Typical conveyor drive assemblies include the following:
Reducers
Torque Arm Type Reducers
The Torque Arm type of reducer is a shaft-mounted reducer with top motor mount and high-speed V belts. This reducer is an excellent fit for a broad range of applications requiring an average reduction ratio.
Motorized Torque Arm
An alternative is the Motorized Torque Arm, a shaft-mounted reducer that utilizes a right angle C-face motor mount (this replaces the top motor mount and high-speed V belts with a directly connected motor).
Shaft-Mounted Reducer with Inline Motor
The Shaft-Mounted Reducer with Inline Motor offers a suitable option for high horsepower and/or high reduction reducers (common in belt feeders).
For applications requiring low horsepower but high reduction, FEECO employs a “gearmotor” type arrangement.
Customizations for Improving Drive Assembly Performance
In addition to the many standard designs available, there are also many ways to further customize the drive assembly to the specific demands of the application at hand.
Backstop Device
A backstop device is employed in order to prevent the load from reversing direction when the motors are switched off.
VFD
VFDs, or Variable Frequency Drives, allow operators to control motor speed as needed.
Vibration and Heat Sensors
Vibration and heat/temperature sensors are an optional component that are becoming more standard, as they are effective in promoting reliability and longevity of drive components.
Mounting Style
Most reducers are of the shaft-mounted design. However, in applications where an especially heavy reducer is utilized, a swing base is often used to reduce the weight load. A rigid low-speed coupling is also typically used in such settings.
In lieu of a shaft-mounted reducer, a foot-mounted reducer can also be utilized. In this case, the reducer is fully supported by the drive base.
Drive Placement
While drive assemblies can be installed at either the head or tail end of the conveyor, head end installation is typically preferred, as this “pulls” the conveyor belt, which is more effective than pushing. When space is limited, it is sometimes beneficial to install the assembly at a point along the conveyor (between the head and tail ends).
In some high-horsepower applications, it may be more economic to install two smaller drive assemblies as opposed to one large one.
Conclusion
Conveyor drive assemblies power bulk material handling equipment in operations of all types. Their dependability, maintainability, safety, and efficiency are crucial factors in minimizing downtime and ensuring overall system efficiency. Their varied application requires careful consideration to expertly match the drive assembly components with the required level of duty, with numerous customizations available.
FEECO provides bulk material handling equipment such as troughed belt conveyors for everything from fertilizers and chemicals to aggregates and ores. Our extensive experience allows us to expertly tailor drive assemblies to the application at hand for a seamless, efficient, and reliable handling system. For more information on our belt conveyors or other bulk material handling equipment, contact us today!